These terms are usually used to contrast the two types of stratified squamous epithelium. Human epiglottis epithelium epithelial lining of the lingual or.
Keratinized Vs Non Keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium. These tissues are specially structured to waterproof and reduction of evaporation by underlying tissues. Transitional epithelium is classified as stratified squamous.
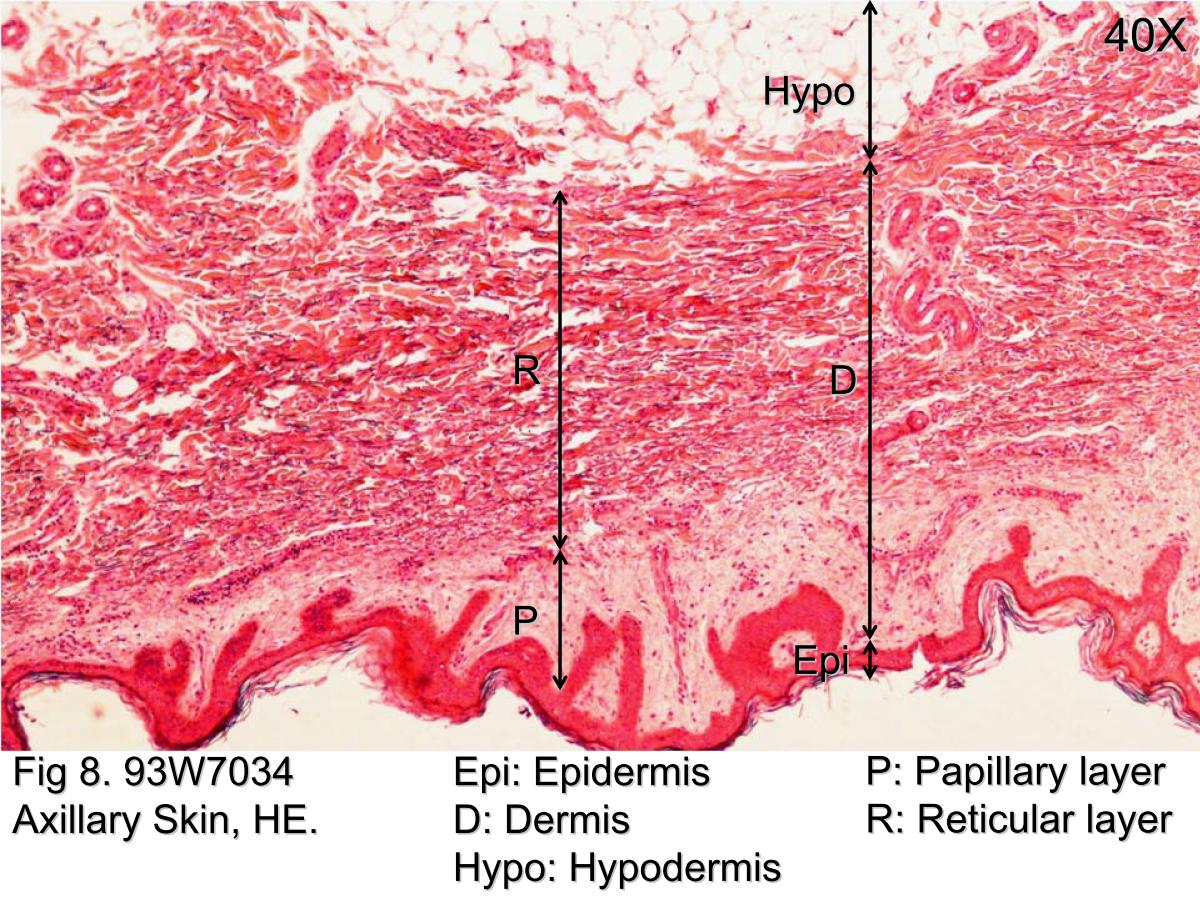 Oral mucosa From slideshare.net
Oral mucosa From slideshare.net
It will form the outer layer of the skin (epidermis) and be either thin (stratified squamous keratinized 1) or thick (stratified squamous keratinized 2). This layer however is not waterproof and affords some degree of protection. These tissues are specially structured to waterproof and reduction of evaporation by underlying tissues.
Oral mucosa
This layer however is not waterproof and affords some degree of protection. The arrow indicates one of these squamous cells. Instead, the distinction lies in the amount of keratinized cells present inside the epithelium because both types actually contain this type of fibrous protein. The keratinized tissues are important for physical abrasion as well as the possibility of desiccation and the loss of water.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
This layer however is not waterproof and affords some degree of protection. Instead, the difference lies in the quantity of keratinized cells current inside the epithelium due to the fact that both types actually contain this kind of fibrous protein. They are filled with a protein called keratin, which is what makes our skin waterproof. It is crucial to realize.
 Source: embryology.med.unsw.edu.au
Source: embryology.med.unsw.edu.au
The non keratinized epithelium forms the lining of the internal surfaces and cavities, which commonly endure friction and physical wear and tear. It will form the outer layer of the skin (epidermis) and be either thin (stratified squamous keratinized 1) or thick (stratified squamous keratinized 2). Keratinized surfaces are protected from absorption by keratin protein. This tissue lines the buccal.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
These terms are usually used to contrast the two types of stratified squamous epithelium. Here’s a comparison of the two. The cells in this tissue are not all squamous (flat). Keratinized surfaces are protected from absorption by keratin protein. Keratinized epithelium has keratin deposited on the surface which makes it.
 Source: bioexplorer.net
Source: bioexplorer.net
The cells of few outer layers of stratified squamous epithetium replace their cytoplasm with a hard water proof protein. This tissue lines the buccal cavity, pharynx and oesophagus. Stratified squamous non keratin epithelium. Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium description provides. A cyst lined by stratified squamous epithelium exhibiting.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
These terms are usually used to contrast the two types of stratified squamous epithelium. Moreover, in keratinized epithelium, the surface cell layer consists of dead cells while in nonkeratinized epithelium, the. This tissue lines the buccal cavity, pharynx and oesophagus. Not only are they flat, but they are no longer alive. Its submitted by organization in the best field.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
The arrow indicates one of these squamous cells. Transitional epithelium is actually stratified squamous epithelium, but there is something special about it. In the digestive system, the stratified squamous epithelium lines the surface of the tongue, the hard upper palate of the mouth, the esophagus, and the anus. The cells in this tissue are not all squamous (flat). Not only.
 Source: anatomy.kmu.edu.tw
Source: anatomy.kmu.edu.tw
Here’s a comparison of the two. Stratified squamous keratinized epithelium 400x (palmar skin) the cells on the surface of stratified squamous keratinized epithelium are very flat. This layer however is not waterproof and affords some degree of protection. These tissues are specially structured to waterproof and reduction of evaporation by underlying tissues. A cyst lined by stratified squamous epithelium exhibiting.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
The keratinized tissues are important for physical abrasion as well as the possibility of desiccation and the loss of water. Epithelium is found in parts of the pharynx, the esophagus, the anal canal, and the vagina. Here’s a comparison of the two. The arrow indicates one of these squamous cells. It is crucial to realize that the difference in between.






