1 and 2 or even 0. 1 [ a] t = k t + 1 [ a] 0 y = m x + b.
Integrated Rate Law Second Order Equation. Additionally, what is the integrated rate law for a first order reaction? Other graphs are curved for azero order reaction.
 Integrated Rate Equation For First Order Reaction From tessshebaylo.com
Integrated Rate Equation For First Order Reaction From tessshebaylo.com
The equation for the second order integrated rate law takes the form y = mx +b, where y = 1/a; The above equation is known as integrated rate equation for zero order reactions. Because this equation has the form y = mx + b, a plot of the inverse of [a] as a function of time yields a straight line.
Integrated Rate Equation For First Order Reaction
Often, the exponents in the rate law are the positive integers: The integrated rate law equation relates concentration and time data. Additionally, what is the integrated rate law for a first order reaction? The order of the differential rate equation, of course, determines the form of the integrated equation.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Tra‑3.c.1 (ek) , tra‑3.c.3 (ek) , tra‑3.c.4 (ek) transcript. When the integrated rate law is written in this way, a plot of ln[a] versus t will yield a. Other graphs are curved for azero order reaction. [a] = −kt+[a]0 y = mx+b [ a] = − k t + [ a] 0 y = m x + b. The integrated.
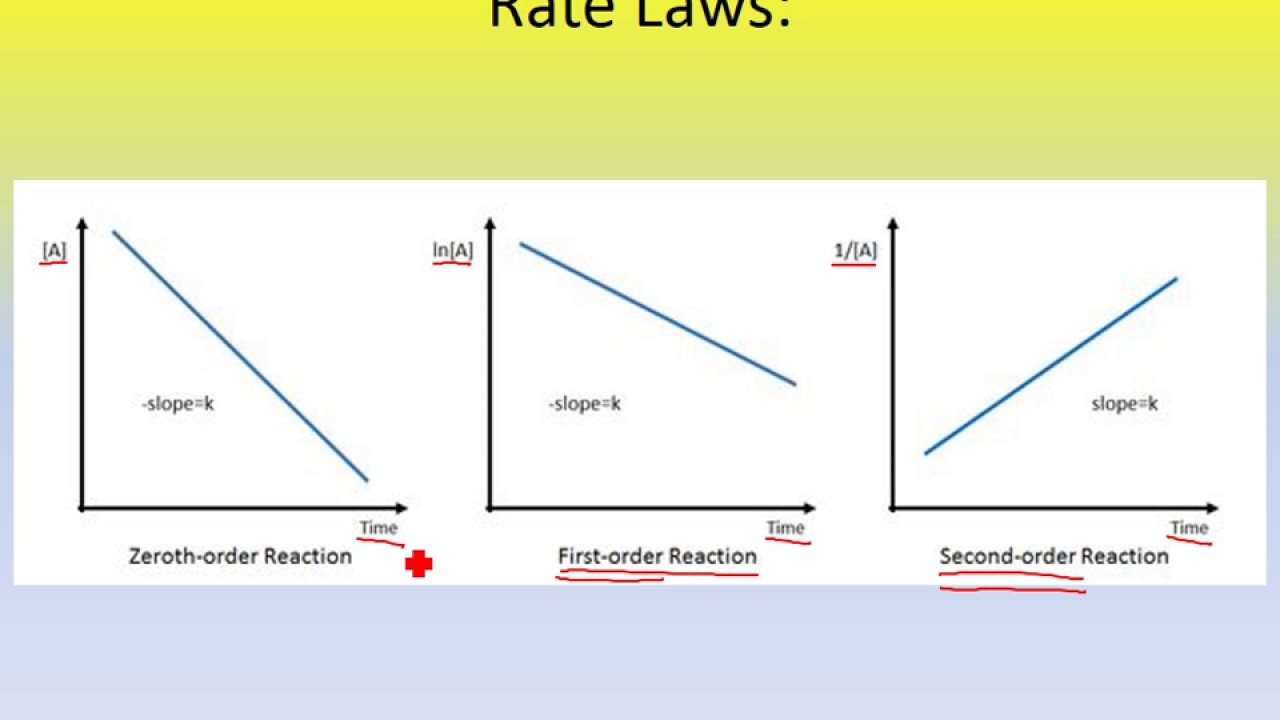 Source: enesa.info
Source: enesa.info
𝑅 p =− [𝑨] 𝒕 = [𝑨] we separate the variables and integrate over the interval: This chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into chemical kinetics. T1/2 = 1 k[r]0 t 1 / 2 = 1 k [ r] 0. Integrated rate law second order equation. 1 and 2 or even 0.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
The rate law expression is a general equation that allows us to relate concentration and rate data. This chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into chemical kinetics. Either the differential rate law or the integrated rate law can be used to determine the reaction order from experimental data. (k = slope of line) examples. Other graphs are curved for.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
The equation for the second order integrated rate law takes the form y = mx +b, where y = 1/a; 1 [a]t = kt+ 1 [a]0 y = mx+b 1 [ a] t = k t + 1 [ a] 0 y = m x + b. 1 and 2 or even 0. ∫ [ ] [ ]2 [𝐴] [𝐴]0.
 Source: tessshebaylo.com
Source: tessshebaylo.com
𝑅 p =− [𝑨] 𝒕 = [𝑨] we separate the variables and integrate over the interval: The order of the differential rate equation, of course, determines the form of the integrated equation. [latex]\frac{1}{[a]} = kt;+;\frac{1}{[a]0}[/latex], [latex]t{1/2} = \frac{1}{[a]_0k}[/latex] chemistry end of chapter exercises describe how graphical methods can be used to determine the order of a reaction and its rate.
 Source: motivatorkerja.com
Source: motivatorkerja.com
Often, the exponents in the rate law are the positive integers: Integrated rate law second order equation. If the plot is not a straight line, then. (k = slope of line) examples. Other graphs are curved for azero order reaction.
 Source: wisc.pb.unizin.org
Source: wisc.pb.unizin.org
Therefore, the required equation for the half life of second order reactions can be written as follows. The above equation is known as integrated rate equation for zero order reactions. If a differential rate law equation is integrated between appropriate limits, the resulting integrated rate law equation shows the dependence of concentration on time. It allows us to determine the..






