Thus, the graph of the second order integrated rate law is a straight. 2a products or a + b products (when [a] = [b]) , rate = k[a] 2 the.
Integrated Rate Law Equation For Second Order Reaction. Differential and integrated rate equation for second order reactions. Thus, the graph of the second order integrated rate law is a straight.
 Chem 2 Chemical V The SecondOrder Integrated From slideshare.net
Chem 2 Chemical V The SecondOrder Integrated From slideshare.net
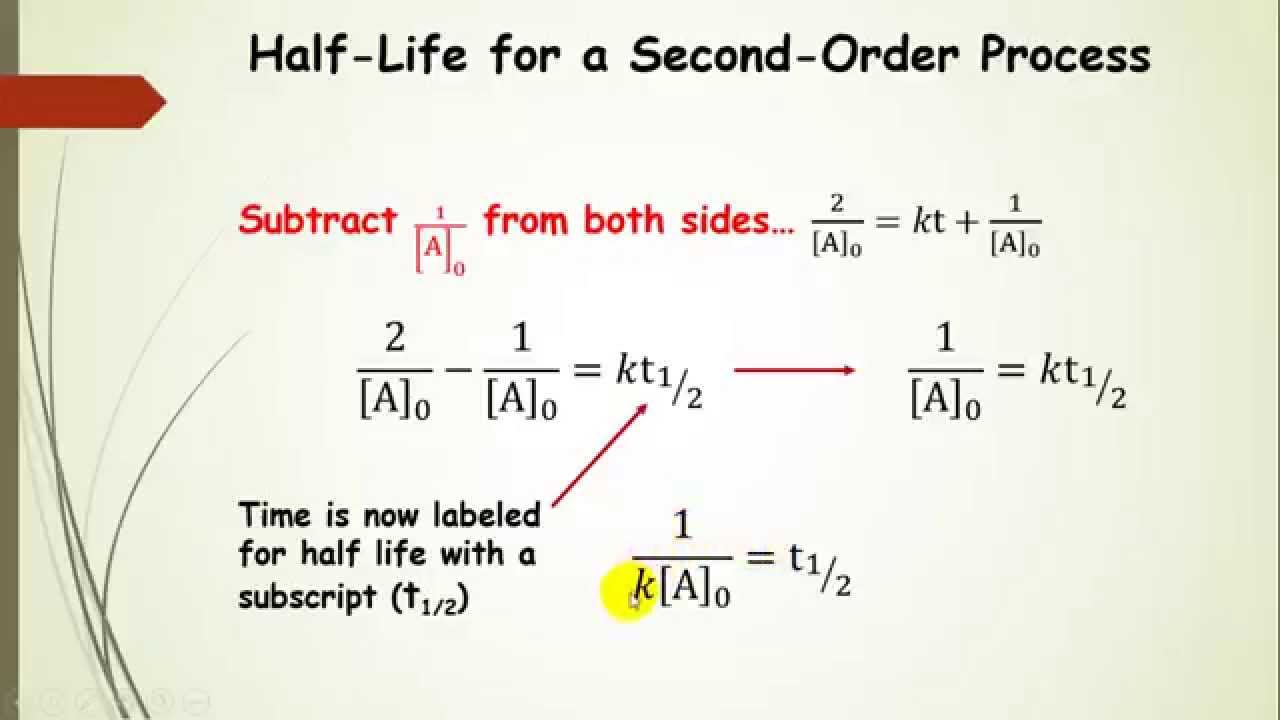
The equation for the second order integrated rate law takes the form y = mx +b, where y = 1/a; 2nd order reaction integrated rate law 1 [𝐴𝐴] = 𝑘𝑘 +𝑑𝑑1 [𝐴𝐴]0 at time t = t1/2 [𝐴𝐴] = 1 2 [𝐴𝐴]0 therefore 1 [𝐴𝐴] = 2 ∙1 [𝐴𝐴]0 substitute for [a] 2 ∙1 [𝐴𝐴0] = 𝑘𝑘𝑑𝑑1⁄2+ 1 [𝐴𝐴]0 rearrange the terms 2 ∙1 [𝐴𝐴0] − 1 [𝐴𝐴0] = 𝑘𝑘𝑑𝑑1⁄2 1 [𝐴𝐴0] On the other hand, integrated rate laws express the reaction rate as a function of the initial concentration and a measured (actual) concentration of one or more reactants after a specific amount of time (t) has passed;
Chem 2 Chemical V The SecondOrder Integrated
The integral form of the equation was obtained from the differential form and the full integration can be found here. They are used to determine the rate constant and the reaction order from experimental data. Integrated rate law second order. 2nd order reaction integrated rate law 1 [𝐴𝐴] = 𝑘𝑘 +𝑑𝑑1 [𝐴𝐴]0 at time t = t1/2 [𝐴𝐴] = 1 2 [𝐴𝐴]0 therefore 1 [𝐴𝐴] = 2 ∙1 [𝐴𝐴]0 substitute for [a] 2 ∙1 [𝐴𝐴0] = 𝑘𝑘𝑑𝑑1⁄2+ 1 [𝐴𝐴]0 rearrange the terms 2 ∙1 [𝐴𝐴0] − 1 [𝐴𝐴0] = 𝑘𝑘𝑑𝑑1⁄2 1 [𝐴𝐴0]
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
[latex]\frac{1}{[a]} = kt;+;\frac{1}{[a]0}[/latex], [latex]t{1/2} = \frac{1}{[a]_0k}[/latex] chemistry end of chapter exercises describe how graphical methods can be used to determine the order of a reaction and its rate constant from a series of data that includes the concentration of a at varying times. On the other hand, integrated rate laws express the reaction rate as a function of the initial.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
If the plot is not a straight line, then the reaction is not second order. Other graphs are curved for azero order reaction. 1 [ a] t = k t + 1 [ a] 0 y = m x + b. 1 [a]t = kt+ 1 [a]0 y = mx+b 1 [ a] t = k t + 1 [.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Second order rate integral rate equation is discussed where a≠bplease like and share. Rate = k[a]0 = k. Thus, the graph of the second order integrated rate law is a straight. Click to see full answer. Integrated rate law second order.
 Source: example—-1.blogspot.com
Source: example—-1.blogspot.com
Differential and integrated rate equation for second order reactions. Considering the scenario where one second order reactant forms a given product in a chemical reaction, the differential rate law equation can be written as follows: Note that the latter can alsobe written: [latex]\frac{1}{[a]} = kt;+;\frac{1}{[a]0}[/latex], [latex]t{1/2} = \frac{1}{[a]_0k}[/latex] chemistry end of chapter exercises describe how graphical methods can be used.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Other graphs are curved for azero order reaction. 1 [ a] t = k t + 1 [ a] 0 y = m x + b. 2nd order reaction integrated rate law 1 [𝐴𝐴] = 𝑘𝑘 +𝑑𝑑1 [𝐴𝐴]0 at time t = t1/2 [𝐴𝐴] = 1 2 [𝐴𝐴]0 therefore 1 [𝐴𝐴] = 2 ∙1 [𝐴𝐴]0 substitute for [a] 2 ∙1.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Thus, the graph of the second order integrated rate law is a straight. The integral form of the equation was obtained from the differential form and the full integration can be found here. [latex]\frac{1}{[a]} = kt;+;\frac{1}{[a]0}[/latex], [latex]t{1/2} = \frac{1}{[a]_0k}[/latex] chemistry end of chapter exercises describe how graphical methods can be used to determine the order of a reaction and its.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
1 [a]t = kt+ 1 [a]0 y = mx+b 1 [ a] t = k t + 1 [ a] 0 y = m x + b. [latex]\frac{1}{[a]} = kt;+;\frac{1}{[a]0}[/latex], [latex]t{1/2} = \frac{1}{[a]_0k}[/latex] chemistry end of chapter exercises describe how graphical methods can be used to determine the order of a reaction and its rate constant from a series of.






