To integrate 2sinx, also written as ∫2sinx dx, we focus on the constant 2 and how it impacts the integration. Integrate sin x dx from x=0 to pi.
Integral Of Sinx Dx. Not only is this a special integral (the sine integral si ( x )), but it also goes from 0 to infinity! This integral is also called the dirichlet.
![Reduction Formula for Integral of [ sin(x) ] ^ n dx YouTube Reduction Formula for Integral of [ sin(x) ] ^ n dx YouTube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/SS7UG32BfsA/maxresdefault.jpg) Reduction Formula for Integral of [ sin(x) ] ^ n dx YouTube From youtube.com
Reduction Formula for Integral of [ sin(x) ] ^ n dx YouTube From youtube.com
Si (x) = ∫ sin (t)/t dt, from t = 0 to t = x. Compute answers using wolfram�s breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals. For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, music…
Reduction Formula for Integral of [ sin(x) ] ^ n dx YouTube
For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, music… Integrate sin x dx from x=0 to pi. Because of the first characteristic, there is no elementary antiderivative and therefore we can’t simply plug the. For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, music…
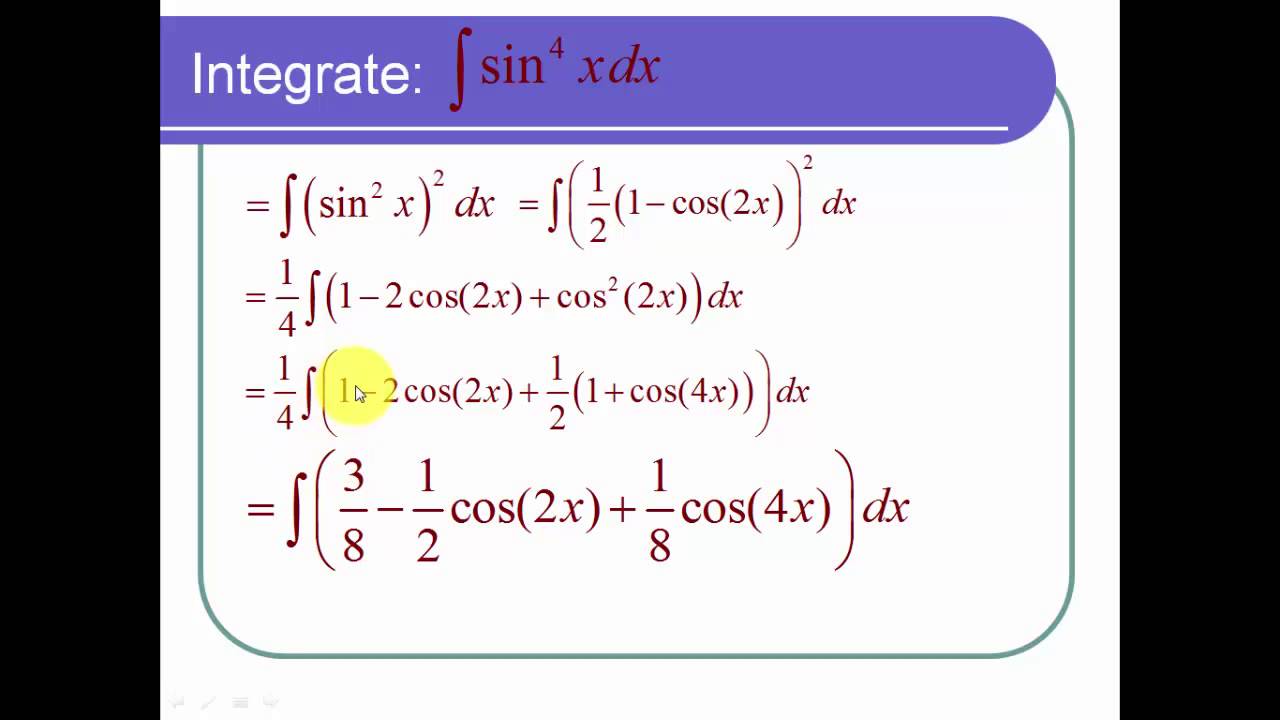 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Sometimes an approximation to a definite integral is desired. Chapter 7 class 12 integrals (term 2) concept wise. ( x) 1 d x = ∫ sin. To integrate 2sinx, also written as ∫2sinx dx, we focus on the constant 2 and how it impacts the integration. Si (x) = ∫ sin (t)/t dt, from t = 0 to t =.
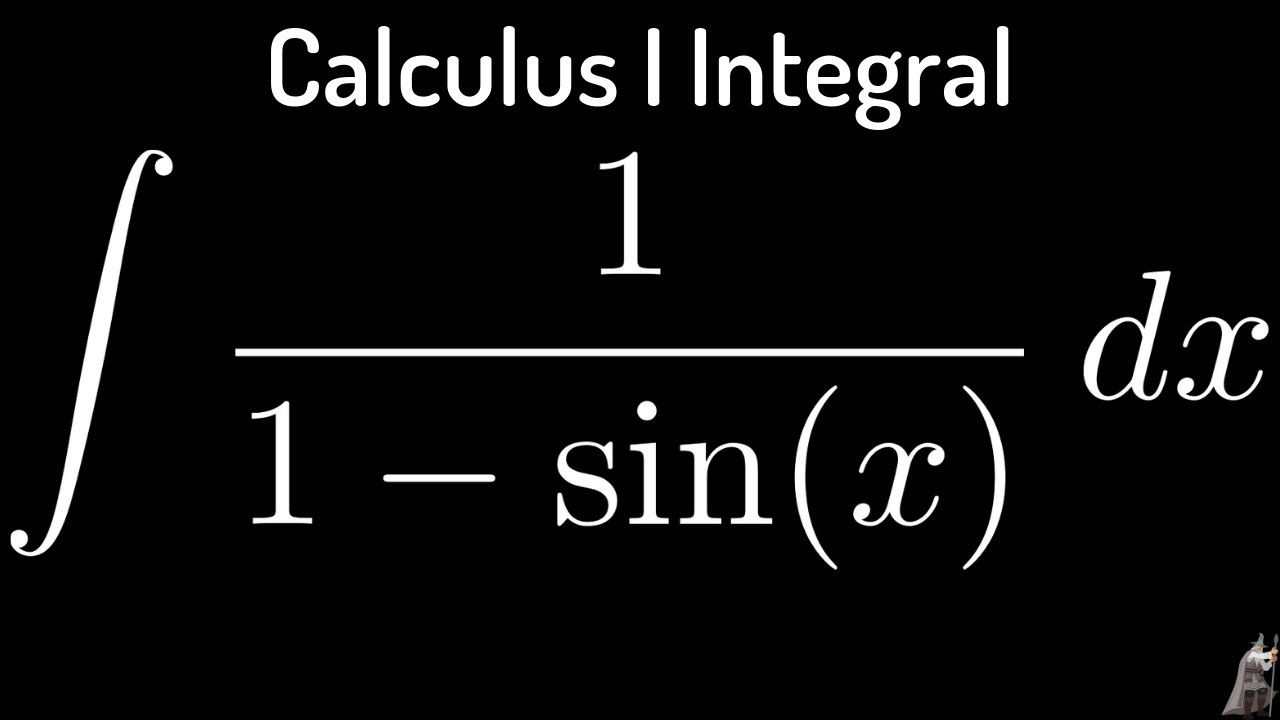 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
$\int \text{fixedsin}(x) = \int 0.75 \ dx = 0.75 \int dx = 0.75x$ but the real $\sin(x)$, that rascal, changes as we go. Approximate antiderivative of sin (x)/x. We recall the pythagorean identity and rearrange it for cos 2 x. ( x) d x = ( − c o s ( π)) − ( − c o s ( 0)).
![Reduction Formula for Integral of [ sin(x) ] ^ n dx YouTube Reduction Formula for Integral of [ sin(x) ] ^ n dx YouTube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/LBqdGn1r_fQ/maxresdefault.jpg) Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Extended keyboard examples upload random. U = x, which implies du/dx = 1. A constant can be brought outside of the integral sign to simplify the integration. The taylor series expansion of sin (x) is. ( x) d x = ( − c o s ( π)) − ( − c o s ( 0)) = 2.
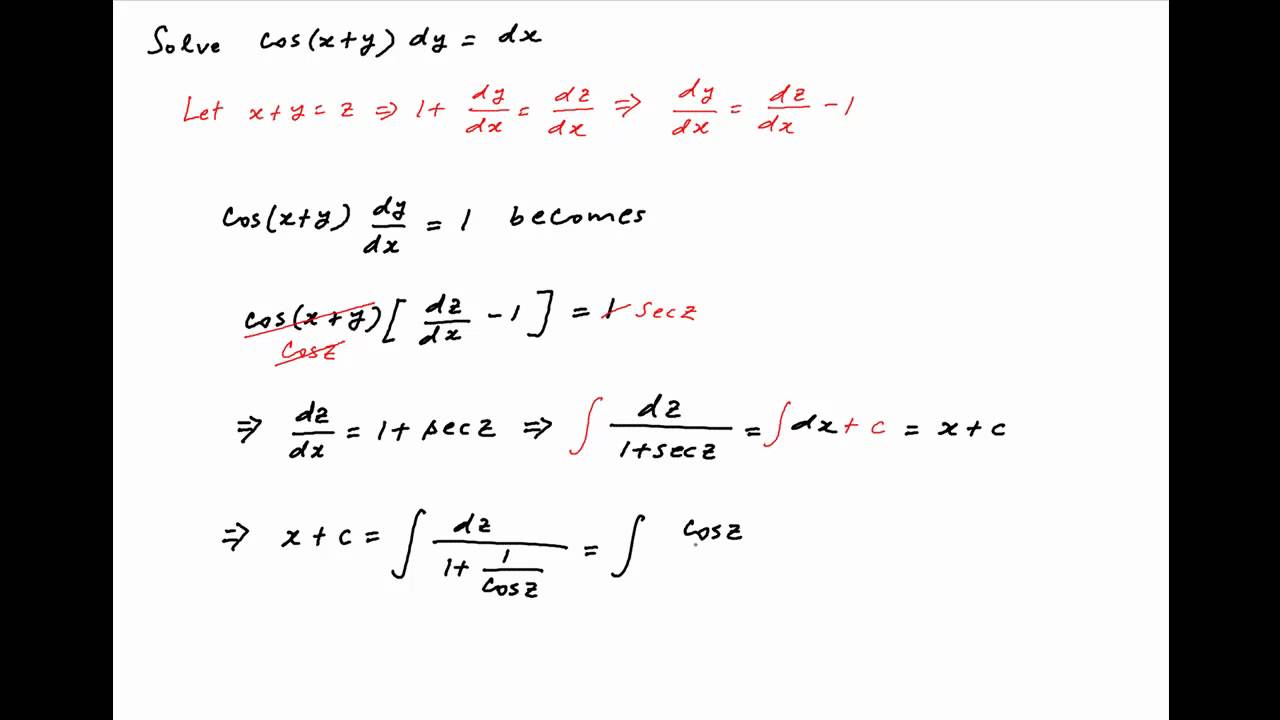 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
This means ∫π 0 sin(x)dx= (−cos(π))−(−cos(0)) =2 ∫ 0 π sin. Answered mar 18, 2021 by tajinderbir (37.1k points) selected mar 18, 2021 by raadhi. If you substitute the values of u, v, du/dx into the standard formula for integration by parts then you get the above expression. The taylor series expansion of sin (x) is. Let x + a.






