Suppose f x( ) is continuous on [ab,]. ∫ ex.dx = ex + c
Integral Formulas Pdf. Integration formulas z dx = x+c (1) z xn dx = xn+1 n+1 +c (2) z dx x = ln|x|+c (3) z ex dx = ex +c (4) z ax dx = 1 lna ax +c (5) z lnxdx = xlnx−x+c (6) z sinxdx = −cosx+c (7) z cosxdx = sinx+c (8) z tanxdx = −ln|cosx|+c (9) z cotxdx = ln|sinx|+c (10) z secxdx = ln|secx+tanx|+c (11) z cscxdx = −ln |x+cot +c (12) z sec2 xdx = tanx+c (13) z csc2 xdx = −cotx+c (14) z I may keep working on this document as the course goes on, so these notes will not be completely
 Formulario de Algebra PDF From resolvemosejerciciosdematematicas.com
Formulario de Algebra PDF From resolvemosejerciciosdematematicas.com
Ex are the anti derivatives (or integrals) of x2 and ex, respectively. 3 + p 2;cos2 ax (69) z cos3 axdx= 3sinax 4a + sin3ax 12a (70) z cosaxsinbxdx=. Common integrals indefinite integral method of substitution ∫ ∫f g x g x dx f u du( ( )) ( ) ( )′ = integration by parts ∫ ∫f x g x dx f x g x g x f x dx( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )′ ′= − integrals of rational and irrational functions 1 1 n x dx cn x n + = + ∫ + 1 dx x cln x ∫ = + ∫cdx cx c= + 2 2 x ∫xdx c= + 3 2 3 x ∫x dx c= +
Formulario de Algebra PDF
∫ ax.dx = ax /loga+ c; View integral formulas.pdf from geed 10223 at polytechnic university of the philippines. Divide [ab,] into n subintervals of width ∆x and choose * x i from each interval. Indefinite integral :∫f x dx f x c( ) = +( )
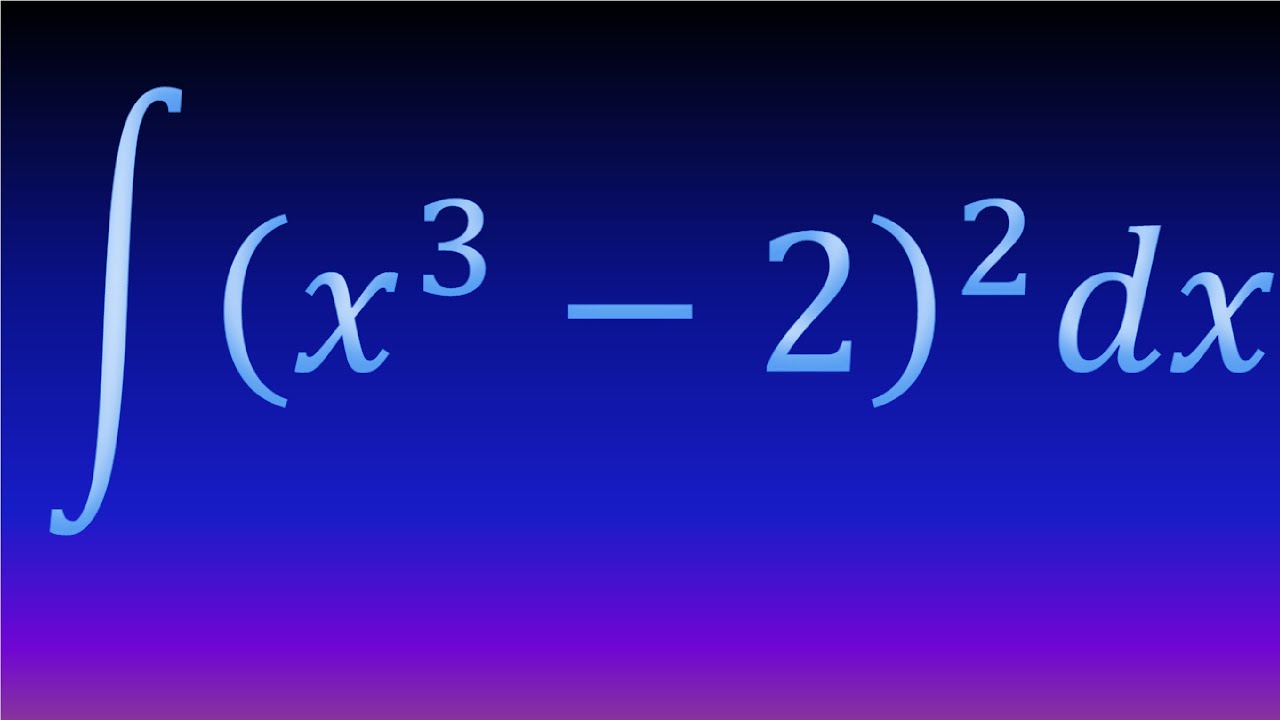 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
2 1 sin ( ) 1 cos(2 )x 2 sin tan cos x x x 1 sec cos x x cos( ) cos( ) x x 22sin ( ) cos ( ) 1xx 2 1 cos ( ) 1 cos(2 )x 2 cos cot sin x x x 1 csc sin x x sin( ) sin( ) x x 22tan.
 Source: librotecarios.blogspot.com
Source: librotecarios.blogspot.com
Substituting u = x−2, u+3=x+1and du = dx, you get z (x+1)(x−2)9dx = z (u+3)u9du = z (u10 +3u9)du = = 1 11 u11 + 3 10 u10 +c = = 1 11 (x−2)11 + 3 10 (x−2)10 +c. 3 2;cos2 ax (75) z cosaxdx= 1 a sinax (76) z cos2 axdx= x 2 + sin2ax. Integrals with trigonometric functions.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
∫1.dx = x + c; ∫ ex[f(x) + f�(x)].dx = ex.f(x) + c; (this just means we nd the antiderivative using ibp and then plug in the limits of integration the way we do with other de nite integrals.) trigonometric integrals for integrals involving only powers of sine and cosine (both with the same argument): If d/dx {φ(x)) = f(x),.
 Source: pinterest.com.mx
Source: pinterest.com.mx
∫1/x.dx = log|x| + c; 7.1 overview 7.1.1 let d dx f (x) = f (x). 3 2;cos2 ax (75) z cosaxdx= 1 a sinax (76) z cos2 axdx= x 2 + sin2ax. If d/dx {φ(x)) = f(x), ∫f(x)dx = φ(x) + c, where c is called the constant of integration or arbitrary constant. Use an appropriate change of variables.
 Source: resolvemosejerciciosdematematicas.com
Source: resolvemosejerciciosdematematicas.com
You can have a look and also download the pdf for both integration and differentiation formulas from below: 3 + p 2;cos2 ax (69) z cos3 axdx= 3sinax 4a + sin3ax 12a (70) z cosaxsinbxdx=. Ρ(x) = 1 σ √ 2π e−x2/2σ2 Integrals with trigonometric functions (71) z sinaxdx= 1 a cosax (72) z sin2 axdx= x 2 sin2ax 4a.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Common integrals polynomials ∫dx x c= + ∫k dx k x c= + 1 1,1 1 x dx x c nnn n = + ≠−+ ∫ + 1 dx x cln x ⌠ = + ⌡ ∫x dx x c−1 = +ln 1 1,1 1 x dx x c nnn n − = +≠−+ ∫ −+ 1 1 dx ax.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Integrals with trigonometric functions z sinaxdx= 1 a cosax (63) z sin2 axdx= x 2 sin2ax 4a (64) z sinn axdx= 1 a cosax 2f 1 1 2; 7.1 overview 7.1.1 let d dx f (x) = f (x). 7.1.3 geometrically, the statement∫f dx()x = f (x) + c = y (say) represents a family of. Then, we write∫f dx()x.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Then ( ) (*) 1 lim i b n a n i f x dx f x x →∞ = ∫ =∑ ∆. Indefinite integrals are antiderivative functions. Indefinite integral :∫f x dx f x c( ) = +( ) ∫ = + ∫ = ∫. ∫ ax.dx = ax /loga+ c;






