Therefore, the instantaneous velocity of the object at any instant t is given by 2 t. Its speed is then said to be variable and its speed at a particular.
Instantaneous Velocity Formula. = instantaneous velocity (m/s) = vector change in position (m) δt = change in time (s) The instantaneous velocity at a point p can be found by making δt smaller and smaller.in this case δx will also become smaller and point q will approach p.if we.
 Ch 2 One Dimensional Kinematics From slideshare.net
Ch 2 One Dimensional Kinematics From slideshare.net
Then, its instantaneous speed is given by. Using calculus, it�s possible to calculate an object�s velocity at any moment along its path. Therefore when calculating instantaneous speed using the limiting process described above for velocity, we get that instantaneous speed at time t is equal to the absolute value of the instantaneous velocity:
Ch 2 One Dimensional Kinematics
Using calculus, it�s possible to calculate an object�s velocity at any moment along its path. The ball will hit ground at the time t = \answer [. Instantaneous velocity formula “instantaneous velocity is total displacement divided by total time as the time interval approaches zero. Its speed is then said to be variable and its speed at a particular instant is called the instantaneous speed.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Instantaneous velocity is a vector, and so it has a magnitude (a value) and a direction. This is equivalent to the derivative of position with respect to time. Insert the values of t 1 = t and t 2 = t + δt into the equation for the average velocity and take the limit as δt→0, we find the instantaneous.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
The relationship is shown as given: Its speed is then said to be variable and its speed at a particular instant is called the instantaneous speed. Instantaneous velocity is a vector, and so it has a magnitude (a value) and a direction. Formula of instantaneous speed is speed(i) = ds dt s p e e d ( i) = d.
 Source: showme.com
Source: showme.com
This is equivalent to the derivative of position with respect to time. This is equivalent to the derivative of position with respect to time. Therefore when calculating instantaneous speed using the limiting process described above for velocity, we get that instantaneous speed at time t is equal to the absolute value of the instantaneous velocity: 2 t + δ t..
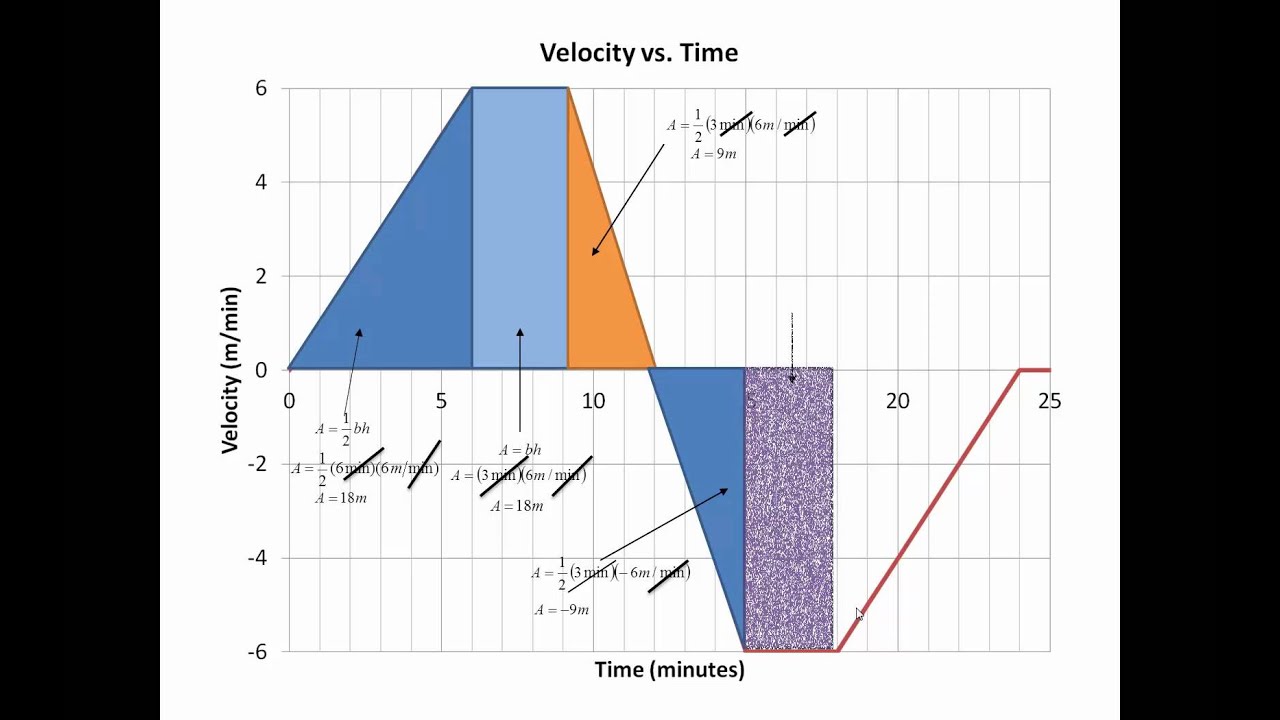 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Like average velocity, instantaneous velocity is a vector with dimension of length per time. As δ t approaches 0, 2 t + δ t approaches 2 t, so we can write: For the first calculation method, consider that a train covers {eq}8:m {/eq} in {eq}0.4:s {/eq}. However, my instantaneous velocity is my velocity at. Instantaneous velocity formula is made use.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
It is the velocity of the object, calculated in the shortest instant of time possible ( calculated as the time interval δt tends to zero ). This equation has two solutions, one of them is t = 0 seconds. Velocity is the rate of change of position over time, so its the derivative of the function. The instantaneous velocity of.
 Source: stickmanphysics.com
Source: stickmanphysics.com
( v_{int} = \lim_{\delta t\to 0} \frac{\delta x}{\delta t} = \frac {dx}{dt} ) wherewith respect to time t, x is the given function. The displacement also approaches zero but the limit of the ratio of displacement to time is. The speedometer in an automobile indicates the instantaneous speed of the automobile. That is, 40 t − 16 t 2 =.






