[ 0, 1 2] x y −8 −6 −4 −2 2 4 6 8 −8 −6 −4 −2 2 4 6 8 for each problem, find the equation of the.
Instantaneous Rate Of Change Equation Calculus. For example, for $f(x,y) = (\operatorname{sin}(πx)\operatorname{cos}(πy), ye^{xy}, x^2+y^3)$ This video contains plenty of examples.
 12 x1 t04 05 displacement, velocity, acceleration (2012) From slideshare.net
12 x1 t04 05 displacement, velocity, acceleration (2012) From slideshare.net
Now, putting x = x 1 then. Instantaneous rate of change at the leftmost value of the given interval. When you are computing the instantaneous rate of change for $f(x,y)$ what do you take the derivative with respect to?
12 x1 t04 05 displacement, velocity, acceleration (2012)
Thus, the instantaneous rate of change at x = 2. Dividing by h leaves (6 + h). Let’s take a look at a specific issue. Its position function is f (x)=16t^2+100.
 Source: present5.com
Source: present5.com
(b) for instantaneous rate of change: Instantaneous rate of change at the leftmost value of the given interval. Graphically, the instantaneous speed is the slope of the tangent line at a specific point. F�(x)=limδx→0 (δy / δx) or, f�(a) =limh→0 {f (a+h) −f (a)} / h. 2 instantaneous rate of change:
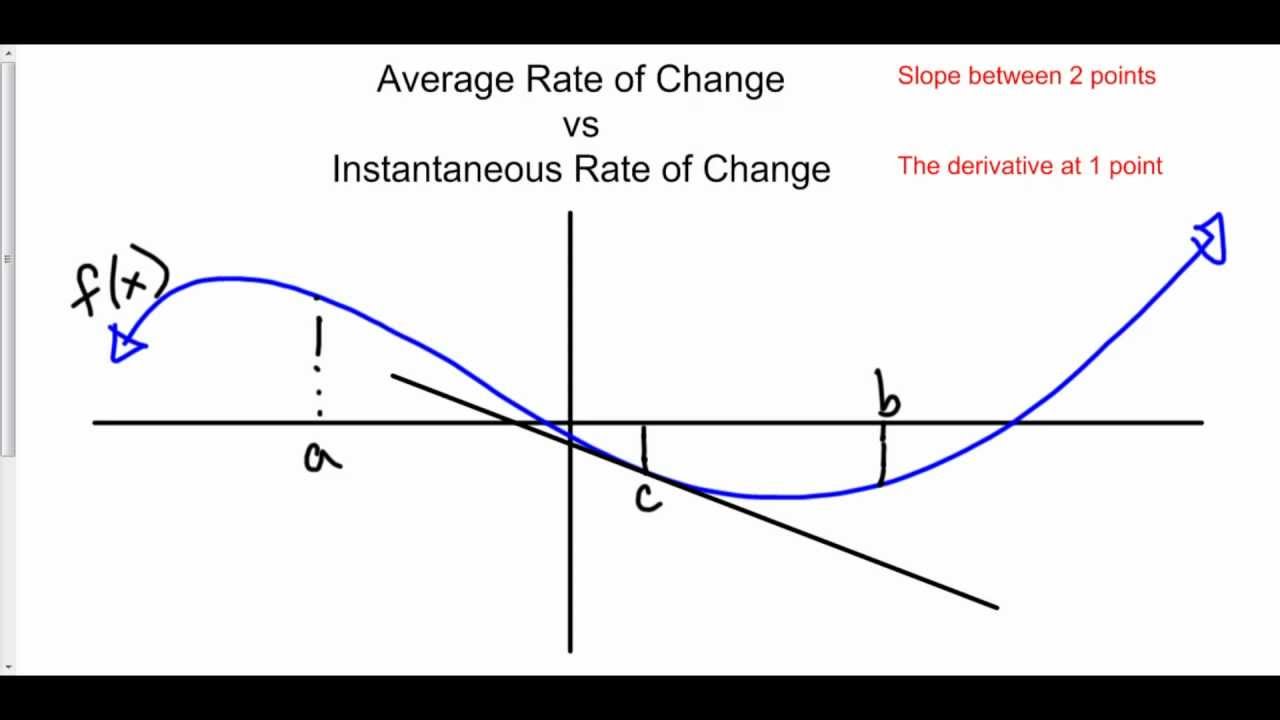 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Thus the instantaneous rate of change formula is. Determine the average velocity between 1 and 3 seconds. Byju’s online instantaneous rate of change calculator tool makes the calculation faster and it displays the rate of change at a specific point in a fraction of seconds. We’re looking for a limit as h→0, so that leaves just 6. Say we have.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Through differentiation, find an equation that relates the instantaneous rate of change of water volume with respect to time to the instantaneous rate of change of water depth at time (t\text{.}) find the instantaneous rate at which the water level is. To determine this instantaneous speed. Spin class heart rate and exercise. Firstly, we’re going to speak about the instantaneous.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Sine function f(x) = sinx (foreshadowing) average rate of change = f(x+ h) f(x) h = sin(x+ h) sinx h = sinxcosh+ cosxsinh sinx h = sinx(cosh 1) + cosxsinh h = sinx cosh 1 h + cosx sinh h the instantaneous rate of change requires us to evaluate the two limits lim This calculus video tutorial shows you how.






