For example, if a car accelerates from rest to 20 m/s in 5 seconds, then its acceleration is given by. Figure 3.14 in a graph of velocity versus time, instantaneous.
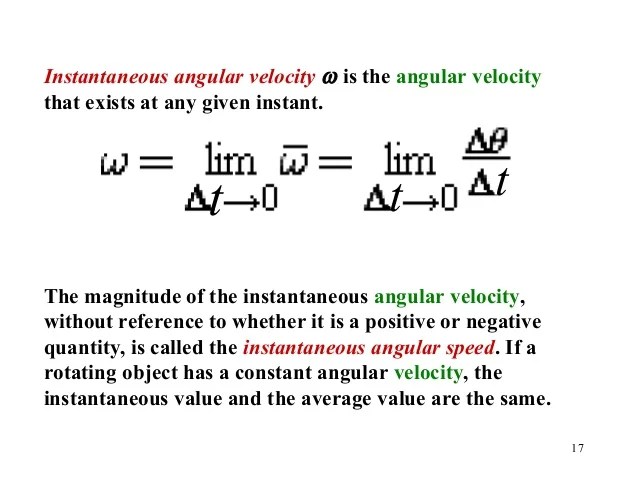
Instantaneous Acceleration Formula. Wherewith respect to time t, x is the given function. Definition and formula for instantaneous acceleration the acceleration a that a particle has at an instant t is equal to the value that the average acceleration , calculated for an interval of time δ t which includes the instant t , approaches as the interval of time δ t gets smaller and smaller, i.e., as δ t approaches 0.
 3 Ways to Calculate Acceleration wikiHow From wikihow.com
3 Ways to Calculate Acceleration wikiHow From wikihow.com
= → = as acceleration is defined as the derivative of velocity, v, with respect to time t and velocity is defined as the derivative of position, x, with. The instantaneous acceleration of an object is the limit of the average acceleration as the elapsed time approaches zero, or the derivative of velocity v with respect to t: Is the change in angular velocity over a time interval.
3 Ways to Calculate Acceleration wikiHow
Since the acceleration is uniform, instantaneous acceleration = average acceleration. The result is the derivative of the velocity function v ( t ), which is instantaneous acceleration and is expressed mathematically as note: So, the acceleration is the change in the velocity, divided. , then average angular acceleration is given by:
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
The distance travelled in 0.7 s, from the graph, is 6mm which means that the. Definition and formula for instantaneous acceleration the acceleration a that a particle has at an instant t is equal to the value that the average acceleration , calculated for an interval of time δ t which includes the instant t , approaches as the interval.
 Source: caroli.org
Source: caroli.org
Now, we can start the. It is expressed in the units of rad/s2 or radians per second squared. The instantaneous acceleration of an object is the limit of the average acceleration as the elapsed time approaches zero, or the derivative of velocity v with respect to t: If we divide dω by dt, we get the instantaneous angular acceleration dα..
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Instantaneous acceleration is thus defined as the acceleration of an object at a specific instant of time. Figure 3.14 in a graph of velocity versus time, instantaneous acceleration is the slope of the tangent line. The instantaneous acceleration of an object is the limit of the average acceleration as the elapsed time approaches zero, or the derivative of velocity v.
 Source: wikihow.com
Source: wikihow.com
= → = as acceleration is defined as the derivative of velocity, v, with respect to time t and velocity is defined as the derivative of position, x, with. Figure 3.14 in a graph of velocity versus time, instantaneous acceleration is the slope of the tangent line. In the special case where the particle undergoes circular motion about the origin,.
 Source: wikihow.com
Source: wikihow.com
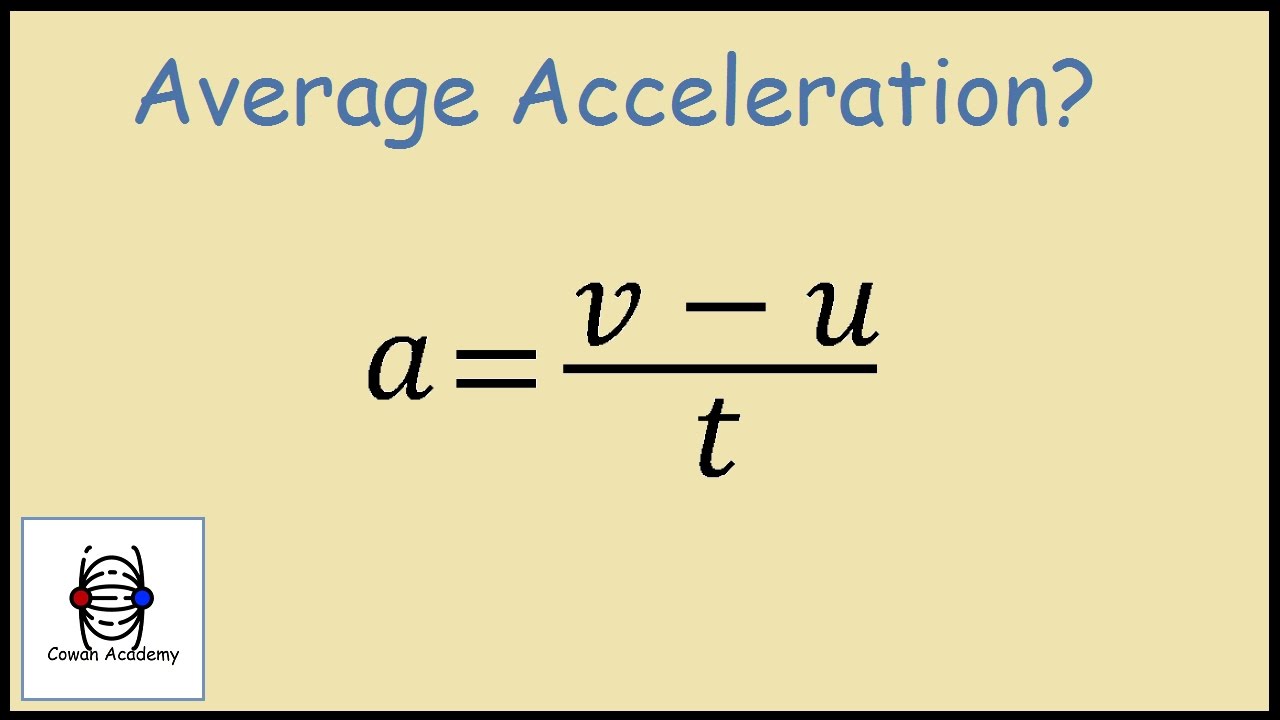
Acceleration formula with solved examples. Figure 3.14 in a graph of velocity versus time, instantaneous acceleration is the slope of the tangent line. Therefore, the formula for average acceleration formula is: When we talk about acceleration, we see that it is the rate of change for velocity. Wherewith respect to time t, x is the given function.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Therefore, the formula for average acceleration formula is: , then average angular acceleration is given by: The distance travelled in 0.7 s, from the graph, is 6mm which means that the. = → = as acceleration is defined as the derivative of velocity, v, with respect to time t and velocity is defined as the derivative of position, x, with..
 Source: wikihow.com
Source: wikihow.com
For example, if a car accelerates from rest to 20 m/s in 5 seconds, then its acceleration is given by. If we divide dω by dt, we get the instantaneous angular acceleration dα. There are two types of acceleration. When we talk about acceleration, we see that it is the rate of change for velocity. A bullet fired in space.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
The instantaneous velocity is articulated in m/s. A avg = δv / δt The formula for acceleration is defined by the change in velocity per unit time i.e. When we talk about acceleration, we see that it is the rate of change for velocity. If we divide dω by dt, we get the instantaneous angular acceleration dα.






