But we can calculate total momentum before inelastic collision by adding their individual momentums using. A collision in which the total momentum and the total kinetic energy are conserved is.
Inelastic Collision Momentum And Kinetic Energy. Examples when the colliding objects stick together after the collision, as it happens when a meteorite collides with the earth, the collision is called perfectly inelastic. An inelastic collision is a collision in which total momentum is conserved but total kinetic energy is not conserved.
 PPT Elastic and Inelastic Collisions PowerPoint From slideserve.com
PPT Elastic and Inelastic Collisions PowerPoint From slideserve.com
(a) two objects of equal mass initially head directly toward one another at the same speed. The momentum before inelastic collision is calculated using the conservation of momentum. Examples of (nearly perfect) elastic collisions are those between billiard balls.
PPT Elastic and Inelastic Collisions PowerPoint
An elastic collision is a type of collision in which the law of conservation of energy and law of conservation of momentum remains conserved. In inelastic collision, there may be deformations of the object colliding and loss of energy through heat. Momentum is conserved, but internal kinetic energy is not conserved. Most of the collisions in daily life are inelastic in nature.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
In this sort of collision, called a perfectly inelastic collision, the colliding objects actually end up stuck together. A collision in which the total momentum and the total kinetic energy are conserved is called an elastic collision. This type of collision is perfectly inelastic because the maximum possible kinetic energy has been lost. Momentum is conserved, but internal kinetic energy.
 Source: teachengineering.org
Source: teachengineering.org
Momentum is conserved in inelastic collisions, but one cannot track the kinetic energy through the collision. A collision in which the total momentum and the total kinetic energy are conserved is called an elastic collision. Billiard ball nboth momentum and kinetic energy are conserved qmost collisions fall between elastic and completely inelastic collisions. An inelastic collision is a collision in.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Examples when the colliding objects stick together after the collision, as it happens when a meteorite collides with the earth, the collision is called perfectly inelastic. First of all, i tell you that i know there is same question available which is already answered, but no answer cleared my doubt, that�s why i. The type of collision in which only.
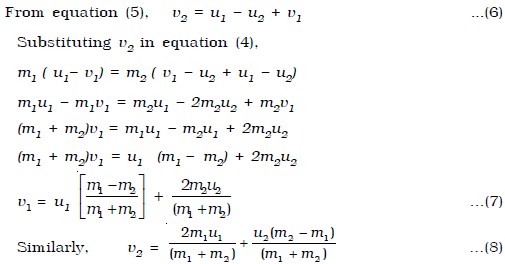 Source: engineersfield.com
Source: engineersfield.com
\frac {1} {2}m {v^2} + \frac {1} {2}m {v^2} = m {v^2} 21. Ki 6˘kf (2.7) where ki and kf. In inelastic collision, there may be deformations of the object colliding and loss of energy through heat. 1 2 m v 2 + 1 2 m v 2 = m v 2. Suppose two similar trolleys are traveling towards each.
 Source: byjus.com
Source: byjus.com
1 2 m v 2 + 1 2 m v 2 = m v 2. An inelastic collision is a collision in which there is a loss of kinetic energy. An inelastic collision is one in which total kinetic energy is not the same before and after the collision (even though momentum is constant). First of all, i tell you.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
For example, the colliding masses can change shape and increase in temperature. • most collisions involve some energy loss, even if the 2.4inelastic collisions inelastic collisions do not conserve energy[4]. This type of collision is perfectly inelastic because the maximum possible kinetic energy has been lost. The kinetic energy is transformed from or into other kinds of energy.






