The collision is inelastic, since energy is not conserved. May be used along with conservation of momentum equation.
Inelastic Collision Formula Physics. In the inelastic collision, the objects stick to each other or move in the same direction. This is because some kinetic energy had been transferred to something else.
 How To Calculate Final Velocity In Elastic Collision From fin3tutor.blogspot.com
How To Calculate Final Velocity In Elastic Collision From fin3tutor.blogspot.com
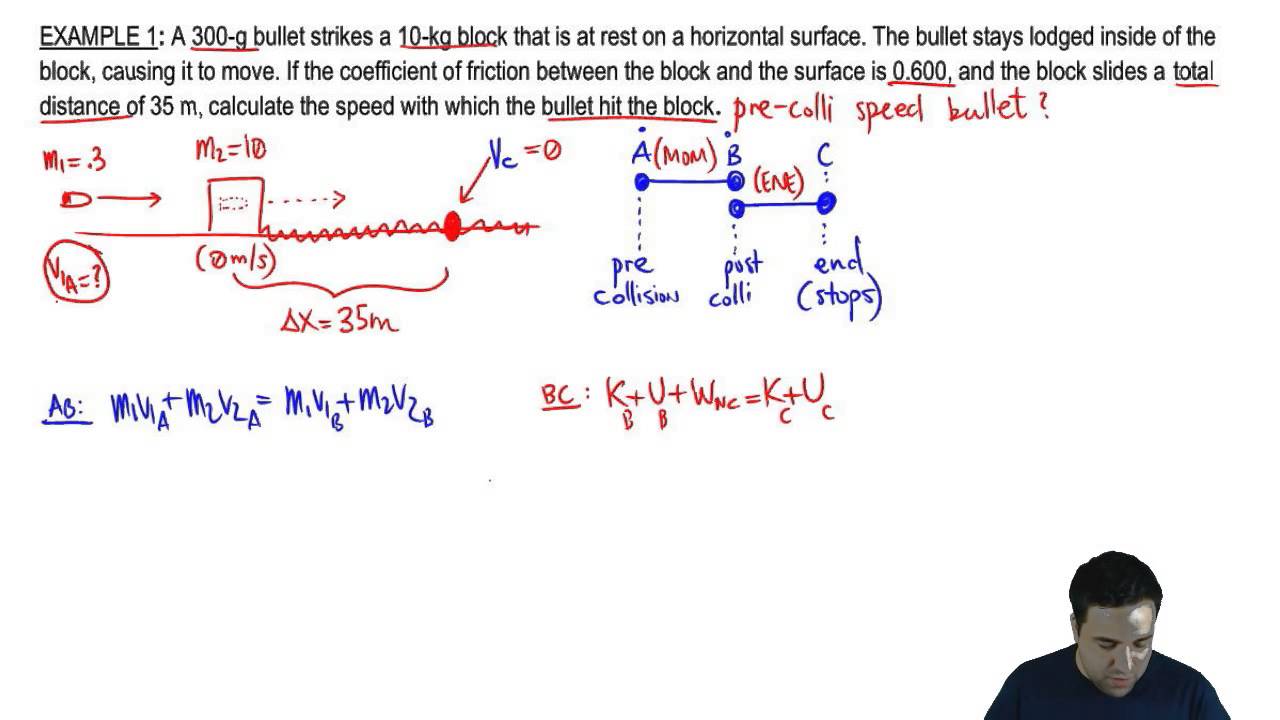
Elastic and inelastic collisions • energy is not conserved in a perfectly inelastic collision. Ke = 1/2 (m) (v)^2. My problem is i don�t know what to do with the spring.
How To Calculate Final Velocity In Elastic Collision
The inelastic collision equation is: The total momentum of the two pucks is zero before the collision and after the collision. In the inelastic collision, the objects stick to each other or move in the same direction. This is because some kinetic energy had been transferred to something else.
![[DH25] 2D Elastic Collision YouTube [DH25] 2D Elastic Collision YouTube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/BZOkrCQRVWM/maxresdefault.jpg) Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Ke = 1/2 (m) (v)^2. May be used along with conservation of momentum equation. • if the objects bounce apart instead of sticking together, the collision is either elastic or partially inelastic. Mass of the stationary object, in kg. (m1) (v1) + (m2) (v2) = (m1 + m2) (vf) where vf is the new velocity and then i would just.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
• if the objects bounce apart instead of sticking together, the collision is either elastic or partially inelastic. May be used along with conservation of momentum equation. A special case of this is sometimes called the perfectly inelastic collision. Mass of object 1 × initial velocity 1 + mass of object 1 × initial velocity 1 = (mass of 1.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Any objects that collide in this way will reduce the total kinetic energy (and total velocity) by this ratio. Mass of object 1 × initial velocity 1 + mass of object 1 × initial velocity 1 = (mass of 1 + mass of 2) × final velocity of combined objects) in. This is because some kinetic energy had been transferred.
 Source: ppt-online.org
Source: ppt-online.org
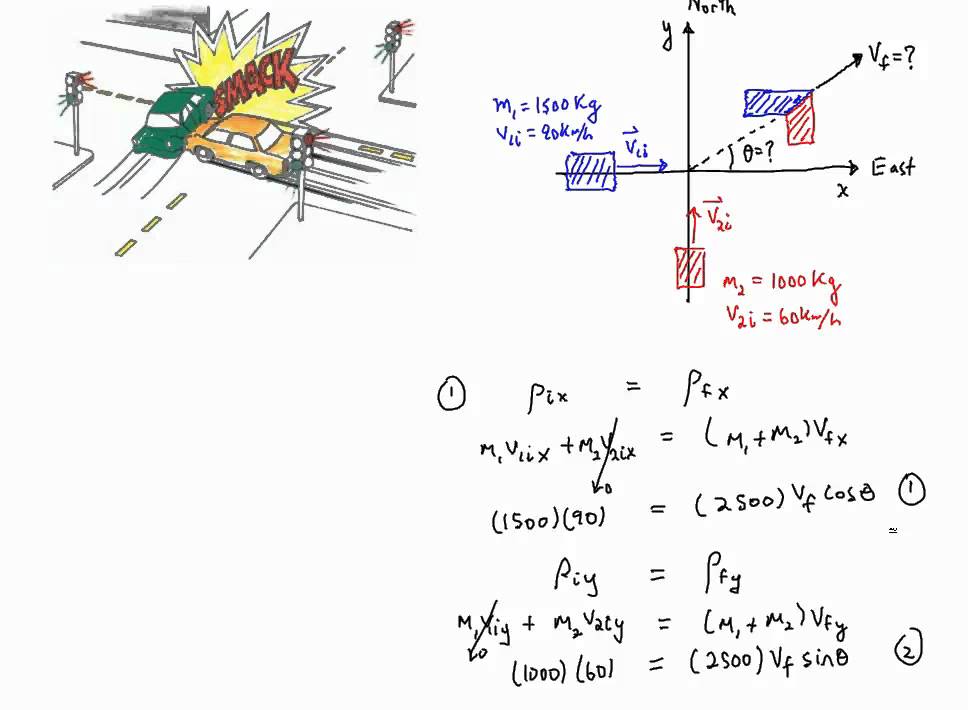
Let particle 1 be the green puck and particle 2 be the blue puck. In the inelastic collision, the objects stick to each other or move in the same direction. Here are a number of highest rated inelastic collision physics pictures on internet. P2 = 0.1 × v1 + 0.2 × v2. Velocity of the moving object, in m/s.
 Source: fin3tutor.blogspot.com
Source: fin3tutor.blogspot.com
Before and after the collision the ratio of the speeds is v 2 /v 1 = m 1 /m 2 = 1/1.2. Velocity of the stationary object after collision, in m/s. Their total internal kinetic energy is initially 1 2mv2 + 1 2mv2 = mv2. Two moving and rotating, uniformly weighted disks perfectly inelastic collide. Velocity of the moving object,.






