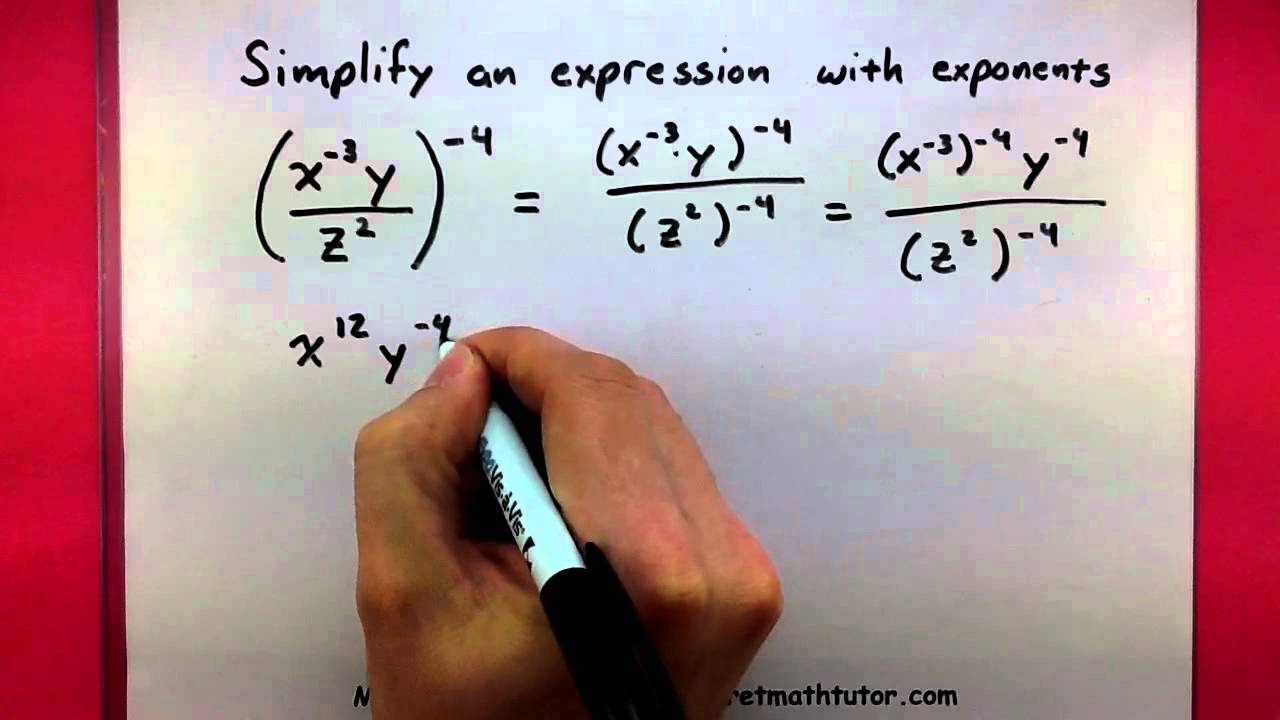It is immobile and inaccessible to plants and is held by force equivalent to a pressure of 30 bar (3. Moisture held firmly as a film on soil particles and.
Hygroscopic Water In Soil. Fine texture soils like clay, clay loam soils contain more hygroscopic water as compared to coarse textured sandy soils. Types of soil water hygroscopic water.
 Soil Water Plant Relationships From slideshare.net
Soil Water Plant Relationships From slideshare.net
Fine texture soils like clay, clay loam soils contain more hygroscopic water as compared to coarse textured sandy soils. Hygroscopic water is on the surface of the soil grains and is not capable of movement by the action of gravity or capillary forces. Source for information on hygroscopic water:
Soil Water Plant Relationships
As this form of water is seen on the particles of soil and not in pores, only some types of soils composed of several pores (such as clays) will comprise a high percentage of it. Hygroscopic moisture content has been linked with many clay mineralogical parameters in predictive geotechnical engineering. Water held by soil under specific relative humidity and temperature conditions (usually 98% relative humidity and 25°c). The hygroscopic coefficient and the maximum capillary capacity are the two equilibrium points when the soil contains the maximum amount of hygroscopic and capillary waters, respectively.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
In platy structure movement of gravitational water is slow and water stagnates in the soil. Thin film of water is tightly held by. The water retained in the pore spaces a. Different types of soil water gravitational water. Just take some soil and pour water onto it.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Types of soil water hygroscopic water. Different types of soil water gravitational water. As this form of water is seen on the particles of soil and not in pores, only some types of soils composed of several pores (such as clays) will comprise a high percentage of it. It is immobile and inaccessible to plants and is held by force.
 Source: geography.name
Source: geography.name
Gravitational water is free water moving through soil by the force of gravity. Hygroscopic moisture is held so strongly by soil particles that plants cannot absorb it. Hygroscopic water is on the surface of the soil grains and is not capable of movement by the action of gravity or capillary forces. Source for information on hygroscopic water: Hygroscopic water is.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Gravitational water is free water moving through soil by the force of gravity. Moisture held firmly as a film on soil particles and not responding to capillary action. The water held tightly on the surface of soil colloidal particles is known as hygroscopic water. This water is essentially unavailable to vegetation. By increasing soil moisture, a thicker membrane is developed.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
The water held tightly on the surface of soil colloidal particles is known as hygroscopic water. It is immobile and inaccessible to plants and is held by force equivalent to a pressure of 30 bar (3. Source for information on hygroscopic water: Held very tightly by the soil particles a. Hygroscopic water is too tightly held by adhesion to be.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Held very tightly by the soil particles a. In platy structure movement of gravitational water is slow and water stagnates in the soil. The water held tightly on the surface of soil colloidal particles is known as hygroscopic water. Hygroscopic water is held so tightly in tiny soil pores by adhesion (a strong attraction between soil particles and water molecules).
 Source: roadex.org
Source: roadex.org
As this form of water is seen on the particles of soil and not in pores, only some types of soils composed of several pores (such as clays) will comprise a high percentage of it. Source for information on hygroscopic water: The hygroscopic coefficient and the maximum capillary capacity are the two equilibrium points when the soil contains the maximum.
 Source: the-compost-gardener.com
Source: the-compost-gardener.com
Granular and crumby structure helps to improve gravitational water movement. Hygroscopic water is tightly bound to soil by adhesion properties, which causes some water only to be consumed by the roots of plants. Hygroscopic water is held so tightly in tiny soil pores by adhesion (a strong attraction between soil particles and water molecules) that roots cannot remove it. The.